The bomb calorimeter works to measure the calorie content of food similarly to that of the coffee cup calorimeter. What is the difference between a coffee cup calorimeter and a bomb calorimeter, in terms of the parameters it can measure?

Bomb calorimeter problems trying to parse out the differences between these two systems.
Coffee cup calorimeter vs bomb calorimeter. Unlike a bomb calorimeter, a coffee cup calorimeter is a constant pressure calorimeter. In a “bomb” calorimeter, reactions occur at constant volume. High temperature reactions because a styraphoam container is going to melt in high temperature, so we�re not going to use that in high temperatures.
Seems to me that most uses for constant pressure calorimetry (coffee cup) involve measuring enthalpy change in solutions, whereas constant volume problems involve measuring enthalpy change from combustion reactions. Q p q_ {p} q p = δh. What is the difference between a coffee cup calorimeter and a bomb calorimeter in terms of the parameters it can measure?
In the textbook,it is said that bomb calorimeter measures the constant volume heat ,while the cup calorimeter measure constant pressure heat.i was wondering, why cup calorimeter is considered constant pressure,even though it also does not allow a gas to expand (it has a fixed volume).so if not then that means cup calorimeter allows some air to get in so that. Now we�re going to look at bomb calorimetry, or isochoric: The bomb calorimeter works at constant.
Which of the following statements are true? Since the coffee cup calorimeter has constant pressure, it. This chemistry video tutorial highlights the difference between the bomb calorimeter and the coffee cup calorimeter.
But bomb calorimeter is also used in high temperature reactions for processes. A) the heat absorbed by the calorimeter is known as the calorimeter constant b) the calorimeter constant is greater than zero c) heat is absorbed only by the water d) in general, the larger the value of the calorimeter constant, the better the. We can substitute these in to show that, under isobaric conditions (like the coffee cup) Δh = q ok, cool.
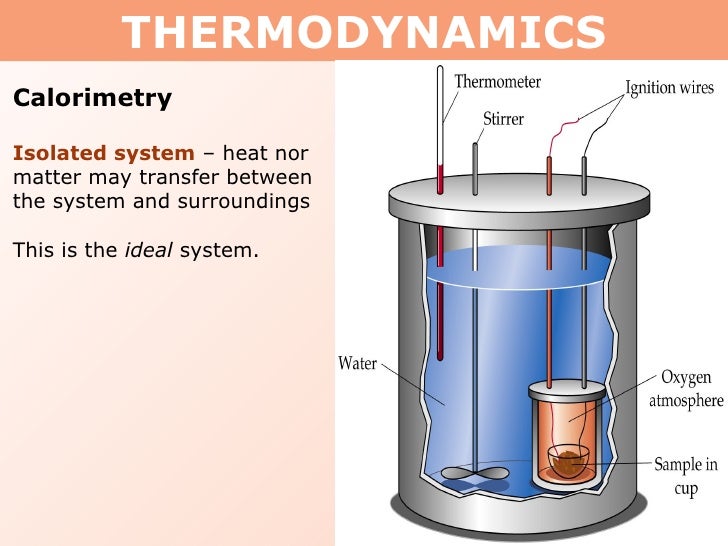
A sample of 1.550 g of liquid hexane (c 6 h 14) undergoes combustion in a bomb calorimeter, and the temperature rises from 25.87 o c to 38.13 o find δe rxn for the reaction in kj/mol hexane. In a coffee cup calorimeter, the reaction takes place in the water, while in a bomb calorimeter, the reaction takes place in a sealed metal container, which is placed in the water in an insulated container. So, to repeat, that is coffee cup, or isobaric.
Both useful, however, the bomb calorimeter is better to use if you�re measuring deltah of a gas. However, it could be that the hardware and the water heat capacities have both been measured and you treat it much like in bomb calorimetry. A bomb calorimeter works in the same manner as a coffee cup calorimeter, with one big difference:
In bomb calorimeters, solids that exhibit low or high temperature reactions are measured in heat flow. Reaction in bomb calorimeter occurs under constant volume \textit {constant volume} constant volume, so it measures δ \delta δ e. The bomb calorimeter works to measure the calorie content of food similarly to that of the coffee cup calorimeter.
We�re going to use a bomb calorimeter for high temperatures. In a “coffee cup” calorimeter, reactions occur at constant pressure. A coffee cup calorimeter consists of a coffee cup, a thermometer, water, and a reactant placed inside the cup.
Coffee cup calorimeter is much easier and probably used much often than a bomb calorimeter. A coffee cup calorimeter consists of a coffee cup, a thermometer, water, and a reactant placed inside the cup. The coffee cup calorimeter is useful for measuring the enthalpy changes that occur in an aqueous reaction since enthalpy is equivalent to the amount of heat energy transferred at constant pressure.
The bomb calorimeter is able to withstand the high temperature reactions of the measuring the calorie content. Bomb calorimeter problems trying to parse out the differences between these two systems. The heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter,.
The bomb calorimeter is useful for measuring the energy of combustion of a substance. What is the difference between a coffee cup calorimeter and a bomb calorimeter, in terms of the parameters it can measure? The bomb calorimeter has constant volume while the coffee cup calorimeter has constant pressure.
What you need a coffee cup calorimeter for is measuring heat flow in a solution containing acids or sugars as opposed to when burning gases in the pot of coffee; The heat capacity of a coffee cup calorimeter is typically taken to be that of the water in the calorimeter. It’s not used to measure the enthalpy change however.
Remember, the initial equation is Δh = Δu + Δ(pv) this time, volume is constant, and so Δ(pv) = vΔp That is if they escape during the boiling process. Unlike a bomb calorimeter, a coffee cup calorimeter is a constant pressure calorimeter.