
In a coffee cup calorimeter, 2.6 g c a c l x 2 ( s) was dissolved in 260 g of water at a combined initial temperature of 23 ∘ c. Science chemistry q&a library in the laboratory a coffee cup calorimeter, or constant pressure calorimeter, is frequently used to determine the specific heat of a solid, or to measure the energy of a solution phase reaction.
Calculate δh for the reaction.
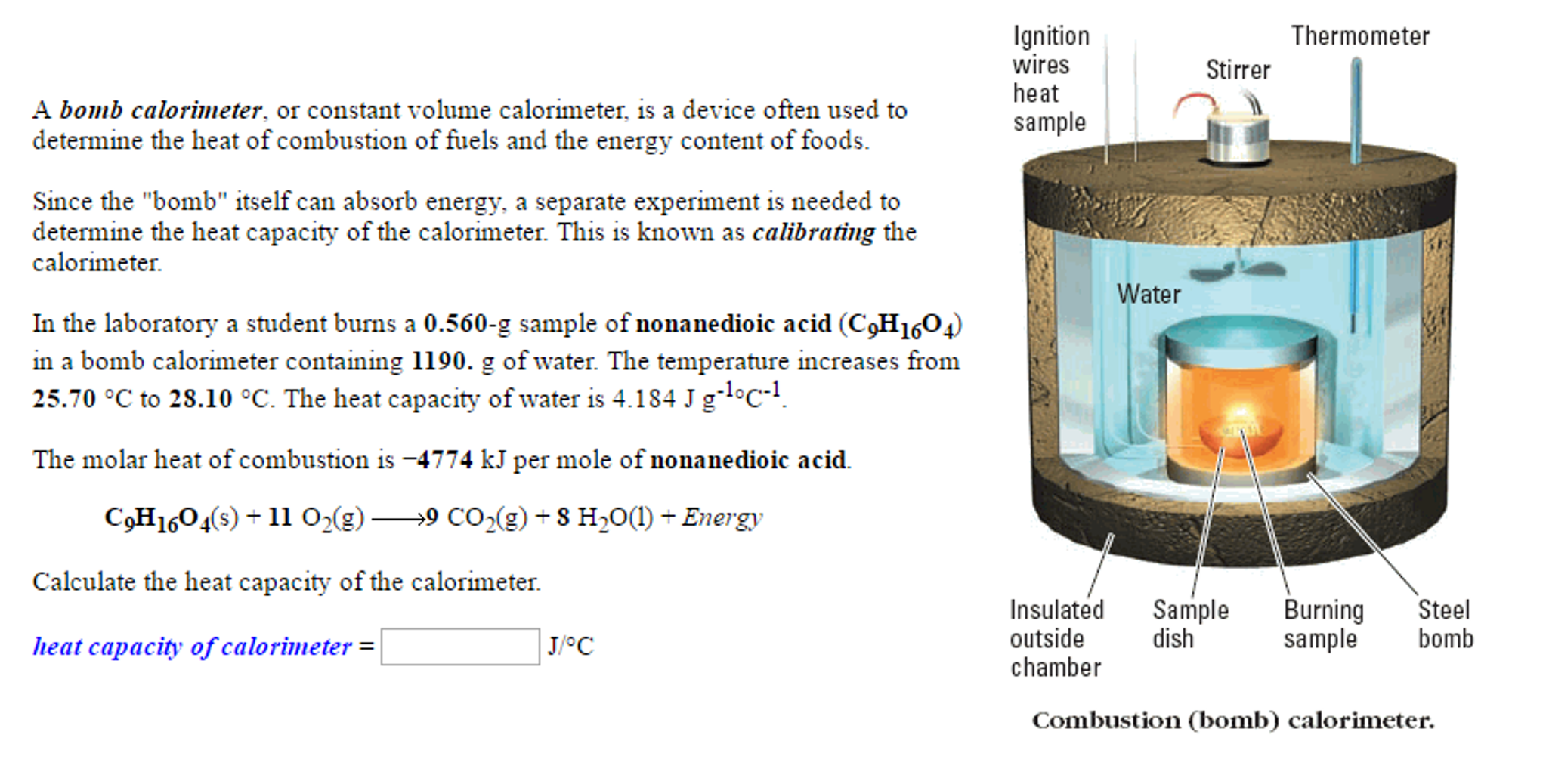
Coffee cup calorimeter problems. The heat capacity of aluminum is 0.900 j/goc. A coffee cup calorimeter consists of a coffee cup, a thermometer, water, and a reactant placed inside the cup. Sample problem #2 (calorimetry) we use a device called a bomb calorimeter to measure the change in the internal energy at constant volume.
Seems to me that most uses for constant pressure calorimetry (coffee cup) involve measuring enthalpy change in solutions, whereas constant volume problems involve measuring enthalpy change from combustion reactions. Let�s look at a bomb calorimeter. Thenmn a student heats 62.11 grams of zinc to 98.17 °c and then drops it into a cup containing 75.89 grams of water at 23.33 °c.
If the final temperature is 26.4 °c, what is the specific heat of aluminum in j/g °c? She first wishes to determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter (ccal) for her coffee cup calorimeter. Sample of water at 25.0 cc.
This chemistry video tutorial explains how to calculate the enthalpy change using a coffee cup calorimeter at constant pressure. It is clear that at least some of the ice is going to melt. In a coffee cup calorimeter, 2.6 g c a c l x 2 ( s) was dissolved in 260 g of water at a combined initial temperature of 23 ∘ c.
In an experiment two students decided to determine the heat capacity of a coffee cup calorimeter. She pours a 50.0 ml sample of water at 72.0 cc into the calorimeter containing a 50.0 ml. H = ms t h = (101 grams soln.) (4.184 j/g °c) (6.45 °c)
What is the final temperature after 840 joules is absorbed by 10.0g of water at 25.0oc? This chemistry video tutorial highlights the difference between the bomb calorimeter and the coffee cup calorimeter. Calculate δh for the reaction.
To measure enthalpy changes, we use what is called calorimetry. Calorimetry is the science of measuring the amount of heat transferred to or from a substance in a reaction by using a calorimeter to measure the heat exchanged with the surroundings. How many grams of water can be heated from 20.0 oc to 75oc using 12500.0 joules?
But in this problem the mass of c a c l x 2 is added to the mass of water: The heat capacity of the apparatus is 10.0 j/k. Trying to parse out the differences between these two systems.
I would really appreciate if someone could explain to me when to include the mass of. Chemical reactions involve the release or consumption of energy, usually in the form of heat.heat is measured in the energy units, joules (j), defined as 1 kg⋅m2/s2. Calculate the final temperature of the water in the cup.
The absolute enthalpy of a system (h) cannot be measured directly. Sulfur (2.56 g) is burned in a bomb calorimeter with excess o2(g). Another common heat unit is the calorie (cal).
The bomb calorimeter works at constant. However, it is possible to measure changes in enthalpy (δh) by measuring temperature changes, which represent heat being lost or gained. A coffee cup calorimeter consists of a coffee cup, a thermometer, water, and a reactant placed inside the cup.
How much energy is needed to change the temperature of 50.0 g of water by 15.0oc? It is defined as the amount of heat required to Coffee cup calorimetry practice problems.
Explain the technique of the calorimetry calculates and interpret the heat and the properties related using the typical data of the calorimetry a technique that we can use to measure the quantity of heat involved in a chemical or physical process is known as calorimetry. Science chemistry q&a library in the laboratory a coffee cup calorimeter, or constant pressure calorimeter, is frequently used to determine the specific heat of a solid, or to measure the energy of a solution phase reaction. Their data determine the heat capacity of the coffee cup calorimeter to be 10.1 j/ degree c.
When a chemical reaction occurs in the coffee cup calorimeter, the heat of the reaction is absorbed by the water. Using this information, calculate the delta h reaction for the first trial of an mg/hcl experiment. This video contains about 1.
The change in water temperature is used to calculate the amount of heat that has been absorbed (used to make products, so water temperature decreases) or evolved (lost to the water, so its temperature increases) in the reaction. The “system” and “surroundings” exchange heat and this heat is what is measured. Up to 24% cash back 32) a student is preparing to perform a senes of calorimetry experiments.
Calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction. If the specific heat capacity of the solution is 4.184 j/°cg, and the heat capacity of the styrofoam cup is negligible, calculate the molar heat of solution of pcl 3 in water. It is important to understand that in calorimetry problems, the substance reacting is the “system” and the water and calorimetry make up the “surroundings”.
The final temperature was 26.4 ∘ c. When measured in coffee cups, an calorimeter can be an excellent way to detect heat flow in a chemical solution, but its use for reactions, such as reactions involving gas that occur when the cup leaks in.